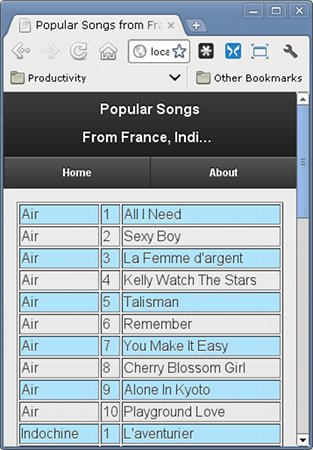
All Android devices have SQLite built-in and, consequently, Android applications can use this SQL database to store and manipulate data.
The SQLiteOpenHelper class needs to be derived and the two following methods implemented:
- onCreate: Called when the database is created for the first time. This is where the creation of tables and the initial population of the tables should happen.
- onUpgrade: Called when the database needs to be upgraded. The implementation should use this method to drop tables, add tables, or do anything else it needs to upgrade to the new schema version.
In addition to the two methods, the constructor also needs to be overrriden to indicate the database name as well as the version (starting at 1; if the database is older, onUpgrade will be used to upgrade the database).
Song Explorer v1
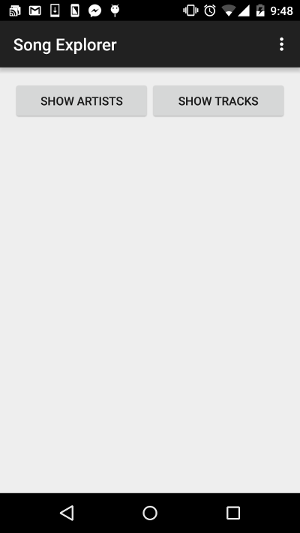
The work to do is to implement the Song Explorer app which will make use of a database to store data about artists and tracks. In version 1 of the app, the artists table will be created and populated with data. There will be two buttons namely Show Artists and Show Tracks. On pressing the Show Artists button, a list of artists will be retrieved from the database and displayed on the screen. Pressing the Show Tracks button will initially provoke an error as the version 1 database only contains information about artists. Version 2 of the app will solve the issue.
Note that two methods of the SQLiteDatabase class are useful here:
- execSQL: for executing inserts, updates and deletes
- rawQuery: for executing an SQL query and returning a Cursor object
Song Explorer v2
In version 2 of the Song Explorer app, we add a new table called tracks and populate it with some data. Since we are changing the database schema, we have to change the database version number and implement the onUpgrade method accordingly. Now, pressing the Show Tracks button displays a list of tracks.
Song Explorer v3
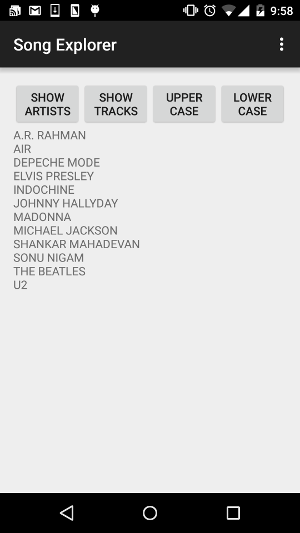
In version 3, we add two new buttons. The first one allows us to change the letters of the artists’ names to uppercase and the second one allows us to change the names to lowercase. While in the two previous versions we were concerned only with retrieving data, here we have to update data.